算法设计手册第二版第五章课后习题解答
列出的解答仅为自己的思路,仅供参考,欢迎指出错误。
题目Wiki及参考答案
http://www.algorithm.cs.sunysb.edu/algowiki/index.php/Graphs-TADM2E
我的解答
遍历
5-6
题目
In breadth-first and depth-first search, an undiscovered node is marked discovered when it is first encountered, and marked processed when it has been completely searched. At any given moment, several nodes might be simultaneously in the discovered state.
(a) Describe a graph on n vertices and a particular starting vertex v such that Θ(n) nodes are simultaneously in the discovered state during a breadth-first search starting from v.
(b) Describe a graph on n vertices and a particular starting vertex v such that Θ(n) nodes are simultaneously in the discovered state during a depth-first search starting from v.
(c) Describe a graph on n vertices and a particular starting vertex v such that at some point Θ(n) nodes remain undiscovered, while Θ(n) nodes have been processed during a depth-first search starting from v. (Note, there may also be discovered nodes.)
解答
(a) Wrost case: 所有的节点都与根节点v直接相连。
(b) Wrost case: 所有的节点的出度都小于等于2,即所有的点都在一条线上。
(c) 非连通图。
5-7
题目
Given pre-order and in-order traversals of a binary tree, is it possible to reconstruct the tree? If so, sketch an algorithm to do it. If not, give a counterexample. Repeat the problem if you are given the pre-order and post-order traversals.
解答
(a) pre-order and in-order
先序遍历特点:第一个节点是根节点。
中序遍历特点:先遍历根节点的左子树,再根节点,然后根节点的右子树。
算法思路:
- 根据先序遍历序列得到root。
- 根据root和中序遍历序列得到左右子树。
- 递归建立左子树。
- 递归建立右子树。
(b) pre-order and post-order
后序遍历特点:先遍历根节点的左子树,再根节点的右子树,然后根节点。
只有先、后遍历序列,无法划分左右子树,无法建立树。
5-8
题目
Present correct and efficient algorithms to convert an undirected graph G between the following graph data structures. You must give the time complexity of each algorithm, assuming n vertices and m edges.
(a) Convert from an adjacency matrix to adjacency lists.
(b) Convert from an adjacency list to an incidence matrix. An incidence matrix M has a row for each vertex and a column for each edge, such that M[i,j]=1 if vertex i is part of edge j, otherwise M[i,j]=0.
(c) Convert from an incidence matrix to adjacency lists.
解答
访问所有的边和点的时间复杂度:
邻接矩阵:O(n2)
邻接链表:O(n+m)
(a) 无向图的邻接矩阵具有对称性,不必遍历整个矩阵。
1 | for x from 1 to n |
需要花费O(n2)从邻接矩阵读数据,然后花费O(n+m)建立邻接链表。
(b) 关联矩阵:形成点和边的映射,矩阵大小为 n·m,建立关联矩阵并初始化需要O(nm)。
1 | edgesx[] // 边i连接的x节点 |
在关联矩阵中为每条边写入数据需要花费O(1),共m条边,需要花费O(m)。从邻接链表读取数据,并检测该边是不是已经记录需要花费O(n+m2),其中检测一条边需要O(m)。因此总的时间花费为O(nm+n+m*m) = O(nm+m2)。
(c) 遍历每一条边,然后插入到邻接矩阵
1 | for j from 1 to m |
遍历需要O(nm),插入需要O(1),故共需要O(nm)。
5-9
题目
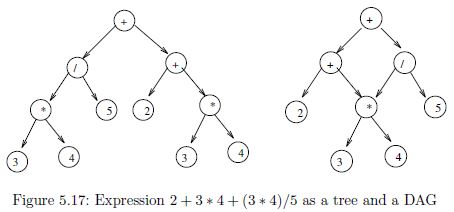
Suppose an arithmetic expression is given as a tree. Each leaf is an integer and each internal node is one of the standard arithmetical operations (+,−,*,/). For example, the expression 2+3*4+(3*4)/5 is represented by the tree in Figure 5.17(a).
Give an O(n) algorithm for evaluating such an expression, where there are n nodes in the tree.
解答
采用递归的方式,获得左子树操作数和右子树操作数,然后做运算,每个节点都会访问一次,时间复杂度O(n)。
假设树节点的定义为:
1 | struct node{ |
1 | calc_tree(root): |
5-10
题目
Suppose an arithmetic expression is given as a DAG (directed acyclic graph) with common subexpressions removed. Each leaf is an integer and each internal node is one of the standard arithmetical operations (+,−,*,/). For example, the expression 2+3*4+(3*4)/5 is represented by the DAG in Figure (see book)(b). Give an O(n+m) algorithm for evaluating such a DAG, where there are n nodes and m edges in the DAG. Hint: modify an algorithm for the tree case to achieve the desired efficiency.
解答
为节点设置一个标记,若已算过该子树,标记设置为true。当再次访问此子树时,可直接获得该子树的结果。再次访问的次数不会超过m,时间复杂度为O(n+m)。
1 | struct node{ |
1 | calc_tree(root): |
5-12
题目
The square of a directed graph G=(V,E) is the graph G2=(V,E2) such that (u,w)∈E2 iff there exists v∈V such that (u,v)∈E and (v,w)∈E; i.e., there is a path of exactly two edges from u to w. square of a graph Give efficient algorithms for both adjacency lists and matrices.
解答
首先,必须清楚这是有向图。
邻接矩阵
这个题目的重点是找到节点v的孙子节点w,连接v与w。如果采用暴力的方法三层for循环遍历邻接矩阵,时间复杂度是O(n3),代价还是很大的,尤其是n比较大,且图G是稀疏图。
如果能有效降低for循环内的次数,虽然时间复杂度是O(n3),但是实际上可能也不会那么高了。
优化方案是为每个节点建立一个队列,那么所有队列的总长度为m(图G边的总数)。这样,遍历该节点的队列就可以得到该节点的孩子。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8for i from 1 to n
for j from 1 to n
if G[i,j] = 1, append(q[i], j) // 将j添加到i的队列中
for i from 1 to n
foreach j in q[i]
foreach k in q[j]
square_G[i,k] = 1构建队列的时间复杂度为O(n2),构建G2的外面两层循环时间复杂度为O(m)。则每个队列的平均长度为 m/n,则内层循环的时间复杂度为O(m/n),总为O(m2/n)。从另外一个角度讲,G2的边数小于2m(你可以试着证明一下,我还不能给出准确的证明),那么
square_G[i,k] = 1的执行次数小于2m。时间复杂度应该为O(n2+m)。邻接链表
现在回想一下,在邻接矩阵的解决方案中,使用的队列,就相当于邻接链表。那我们就省去了构建队列的时间,时间复杂度O(m)。
1
2
3
4for i from 1 to n
foreach j in g->edges[i]
foreach k in g->edges[j]
insert_edges(square_g->edges, i, k, TRUE)
5-13
题目
A vertex cover of a graph G=(V,E) is a subset of vertices V′ such that each edge in E is incident on at least one vertex of V′.
(a) Give an efficient algorithm to find a minimum-size vertex cover if G is a tree.
(b) Let G=(V,E) be a tree such that the weight of each vertex is equal to the degree of that vertex. Give an efficient algorithm to find a minimum-weight vertex cover of G.
(c) Let G=(V,E) be a tree with arbitrary weights associated with the vertices. Give an efficient algorithm to find a minimum-weight vertex cover of G.
解答
(a) 解决思路如下:
叶节点l是不能要的,因为一个叶节点才连一条边,性价比太低了。
那就需要叶节点的父节点p。
p的父节点也就不需要了。
删除p子树,就会得到一颗新的树。重复操作,直到得到空树或只有一个节点的树。
怎么证明,该算法得到的就是最小的集合?
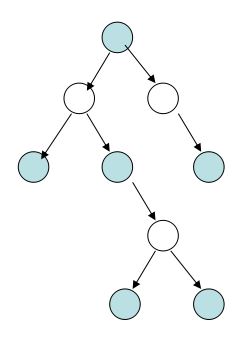
因为我们每次移去的子树,都尽量以一个中心节点,带走尽量多的边,那么最后得到的节点的集合,必然是最小的。插图如下(以2叉树做例子):
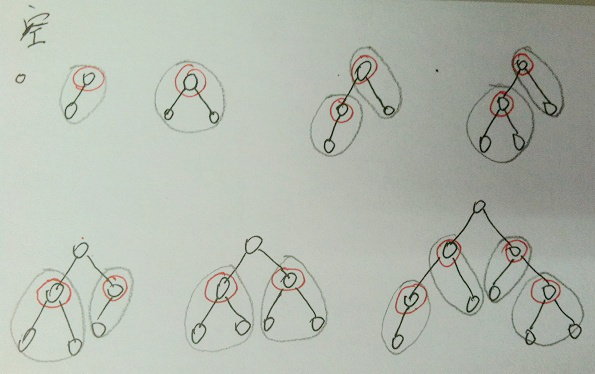
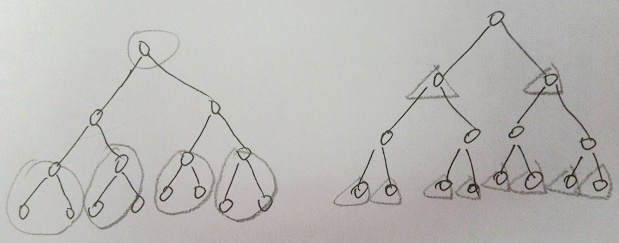
(b) 任何一条边在V’中至少有一个节点,那么V’中所有节点的度的和sum至少为m(图G的边的总数)减少V’中相邻节点的数量,就能降低sum的值。使用(a)中的方法,可以尽量降低sum的值,因为在(a)中选择的点尽量是隔代选择。另外的隔代选择方案是吧叶节点以及他们的父亲的父亲作为目标节点,得到的V’同样是尽量小的。
(c) 待定
要把树作为有向图处理吗?虽然我们把树表示成带箭头的,但是树是无向图,维基百科。
5-14
题目
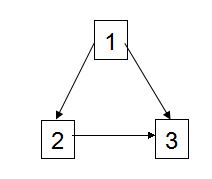
A vertex cover of a graph G=(V,E) is a subset of vertices V′∈V such that every edge in E contains at least one vertex from V′. Delete all the leaves from any depth-first search tree of G. Must the remaining vertices form a vertex cover of G? Give a proof or a counterexample.
解答
否定。反例:
下图得到的DFS序列可以是[1, 3, 2],叶节点为2,3。那么V’={1}。并不是一个顶点覆盖。
5-15
题目
A vertex cover of a graph G=(V,E) is a subset of vertices V′∈V such that every edge in E contains at least one vertex from V′. An independent set of graph G=(V,E) is a subset of vertices V′∈V such that no edge in E contains both vertices from V′.
An independent vertex cover is a subset of vertices that is both an independent set and a vertex cover of G. Give an efficient algorithm for testing whether G contains an independent vertex cover. What classical graph problem does this reduce to?
解答
着色问题。愣是没有想到。
5-16
题目
An independent set of an undirected graph G=(V,E) is a set of vertices U such that no edge in E is incident on two vertices of U.
(a) Give an efficient algorithm to find a maximum-size independent set if G is a tree.
(b) Let G=(V,E) be a tree with weights associated with the vertices such that the weight of each vertex is equal to the degree of that vertex. Give an efficient algorithm to find a maximum independent set of G.
(c) Let G=(V,E) be a tree with arbitrary weights associated with the vertices. Give an efficient algorithm to find a maximum independent set of G.
解答
(a) 基于5-15给出的答案。我们可以先把图着色,然后遍历得到不同颜色的序列,去较短的序列作为最小的独立集合。若不能着色,则不存在最小独立集合。
(b) 有以下几点需要注意:
- 树肯定是可以着色的。
- 着色方案是固定的:孩子与父亲是相反的颜色。
- 题目要求找到最大的独立集合。
先着色,进行一次遍历,将不同颜色的放入两个序列,取总度的和较大者。
不进行着色的处理方案:设置root颜色为0,则其子为1。递归遍历左右子树,时间复杂度为O(n)。
1 | void classify(root, color): |
- (c) 与(b)的不同仅仅是最后,取权重的和的较大者。
5-17
题目
Consider the problem of determining whether a given undirected graph G=(V,E) contains a triangle or cycle of length 3.
(a) Give an O(|V|3) to find a triangle if one exists.
Improve your algorithm to run in time O(|V|·|E|). You may assume |V|≤|E|.
(b) Observe that these bounds gives you time to convert between the adjacency matrix and adjacency list representations of G.
解答
(a) Brute force。
1
2
3
4
5
6for each inode in V do
for each jnode in Adj[inode] do
for each knode in Adj[jnode] do
for each lnode in Adj[knode] do
if lnode = inode then
return true时间复杂度是O(n4),看样子不符合题目的要求。
(b) DFS。
DFS可以发现图中的环,那么当检测到环时,可以进进一步检测环的大小是否为3.采用的就是DFS一次遍历,因此时间复杂度是O(|V|+|E|)。
1
2
3
4process_edge(v, y):
if parent[parent[x]] = y then
is_triangle = true
finish = truegithub仓库源码及测试数据:传送门–>
5-18
题目
Consider a set of movies M1, M2, … , Mk. There is a set of customers, each one of which indicates the two movies they would like to see this weekend. Movies are shown on Saturday evening and Sunday evening. Multiple movies may be screened at the same time. You must decide which movies should be televised on Saturday and which on Sunday, so that every customer gets to see the two movies they desire. Is there a schedule where each movie is shown at most once? Design an efficient algorithm to find such a schedule if one exists.
解答
问题原型:着色问题。把相邻的顶点安排在不同的时间。
最好的情况是符合着色问题,那么每个电影只需要放一遍。因此我们可以使用着色问题的算法解决这个问题,当着色失败时,则不存在这样最优的调度算法。
思考:与着色问题不同的是电影可以放两次,怎样才能让总播放的次数达到最小呢?
电影可以放两次就相当于让一个点拥有两个颜色,在着色的过程中如果出现冲突,将此点标记为double-color,与他相连的还未着色的点可以是任意的颜色,那么如何才能保证全局最小呢?
5-19
题目
The diameter of a tree T=(V,E) is given by max u,v∈Vδ(u,v) (where δ(u,v) is the number of edges on the path from u to v). Describe an efficient algorithm to compute the diameter of a tree, and show the correctness and analyze the running time of your algorithm.
解答
最长路径。
称diameter最顶层的节点定义了diameter。那么对任意节点都存在两种情况:
- 该节点定义了diameter。
- 该节点的任一子节点定义了diameter。
1 | diameter(tree): |
5-20
题目
Given an undirected graph G with n vertices and m edges, and an integer k, give an O(m+n) algorithm that finds the maximum induced subgraph H of G such that each vertex in H has degree ≥k, or prove that no such graph exists. An induced subgraph F=(U,R) of a graph G=(V,E) is a subset of U of the vertices V of G, and all edges R of G such that both vertices of each edge are in U.
解答
寻找最大的导图。特性:
- U中所有顶点的度>=K。
- R中所有边的顶点都在U中。
假设图的存储使用的是邻接链表。
暴力方法:
一次基础遍历得到符合条件的队列O(n+m),排序O(nlogn)。
再次基础遍历O(n+m)看该节点的相邻节点在不在队列之中O(logn)。
借助DFS:
思想:
- 所有的边都遍历一次,然后判断是否符合要求。
- 不使用课本提供的DFS框架,使用简化的DFS。
- 发现新顶点时,递归新的顶点。
- 若该点已被发现但还未处理,处理边(v,y),这样确保了所有的边只处理一遍。
Github:传送门。
5-21
题目
Let v and w be two vertices in a directed graph G=(V,E). Design a linear-time algorithm to find the number of different shortest paths (not necessarily vertex disjoint) between v and w. Note: the edges in G are unweighted.
解答
有向图的最短段路径。